Behold!
Since time immemorial, people on Earth have looked at the night sky and observed countless celestial bodies move through space.
Numerous ancient civilizations looked at the stars and built massive monuments honoring mythical deities that supposedly came from heaven. Orion, Sirius, the Pleiades are just some of the many stars observed by the ancients.
But what are the brightest stars in the night sky, other than our Sun, which is the brightest star in the sky?
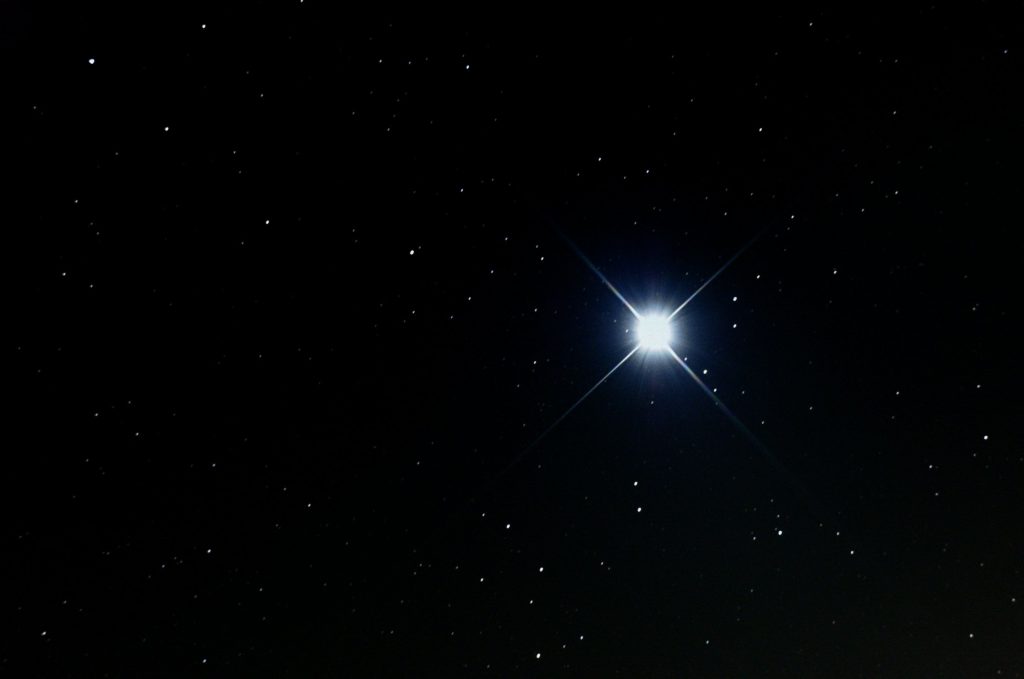

(1) Sirius (Alpha Canis Majoris) is the brightest Star in the entire night sky. Located to the South of celestial Ecuador, at around -16.7º, it is visible practically from all over the planet. Radiating a white color, with a magnitude of -1.5 and at a distance of about eight light-years, is the main star of the Canis Major constellation, which is why it is also known as the Dog Star. It was one of the most important stars in the night sky for civilizations like the Egyptians, as it marked the beginning of the floods of the Nile.
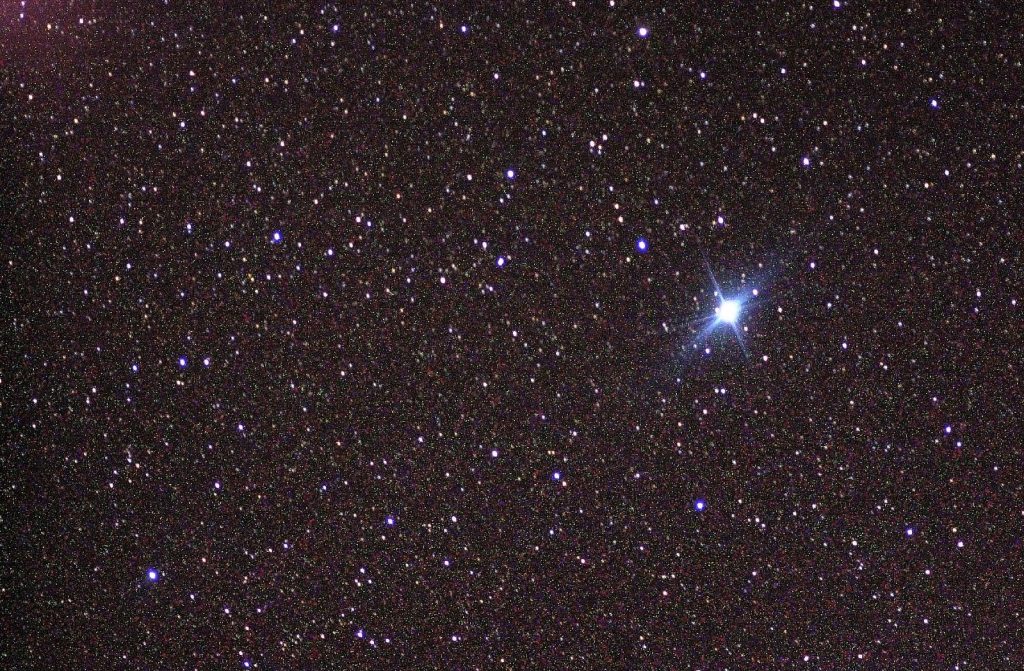

(2) Canopus, also referred to as α Carinae, is the brightest Star in Carina’s southern constellation. It is the second-brightest Star in the night sky, after Sirius. Canopus has a visual magnitude of -0.72. Canopus is essentially white when seen with the naked eye. Canopus was not visible to the mainland ancient Greeks and Romans; it was, however, visible to the ancient Egyptians. It is not visible from anywhere in Europe.
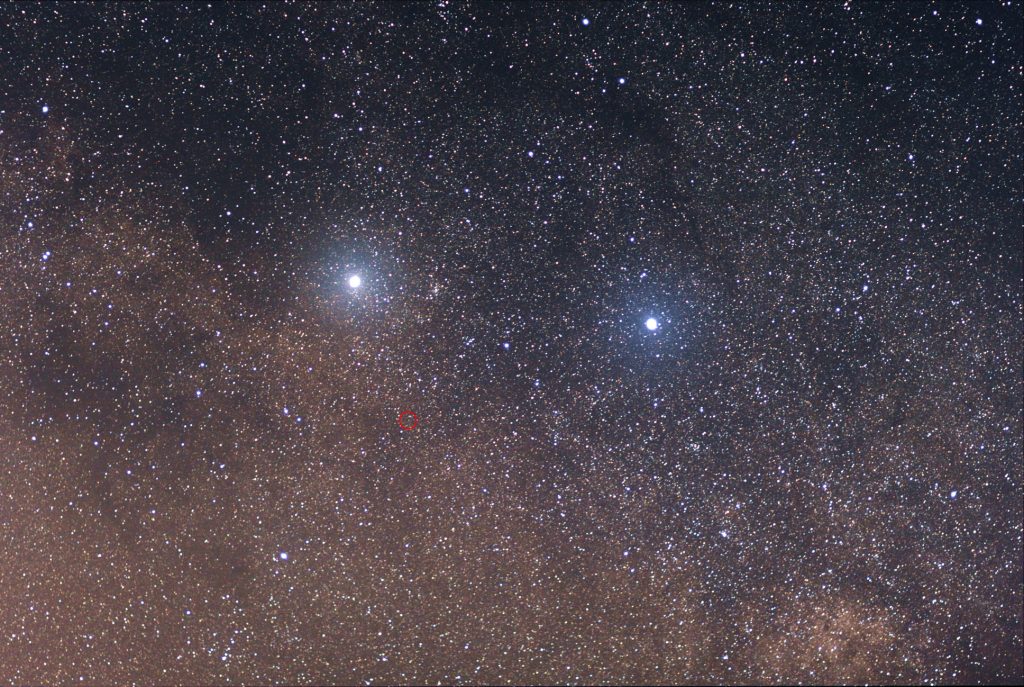

(3) Rigil Kentaurus, more commonly known as Alpha Centauri, is the third brightest Star in the night sky. Alpha Centauri is also the closest star system to Earth, at 4.37 light-years (1.34 pc) from the Sun. Alpha Centauri is a triple star system: α Centauri A, α Centauri B, and α Centauri C, respectively Rigil Kentaurus, Toliman, Proxima Centauri, where astronomers say an Earth-like planet capable of hosting life as we know it may exist.
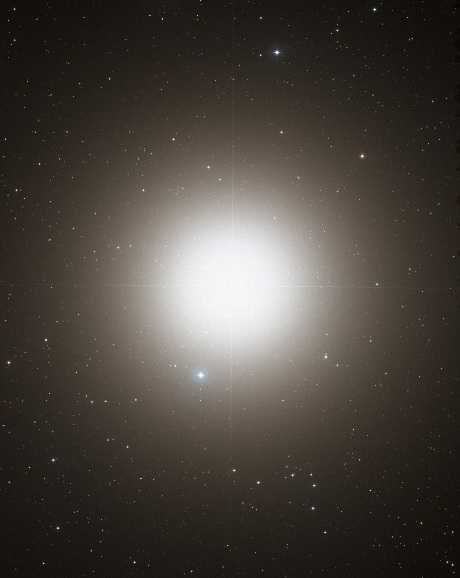

(4) With an apparent visual magnitude of −0.05, Arcturus, aka Alpha Bootis, is the fourth brightest Star in the night sky. It is the brightest in the northern celestial hemisphere. Located at a distance of 36.7 light-years from the Sun, Arcturus is a red giant.

(5) Vega, also called Alpha Lyrae, is the brightest Star in Lyra’s constellation and the fifth brightest Star in the night sky. At a distance of 25 light-years from the Sun, together with Arcturus and Sirius, Vega is one of the most luminous stars in the Sun’s neighborhood.
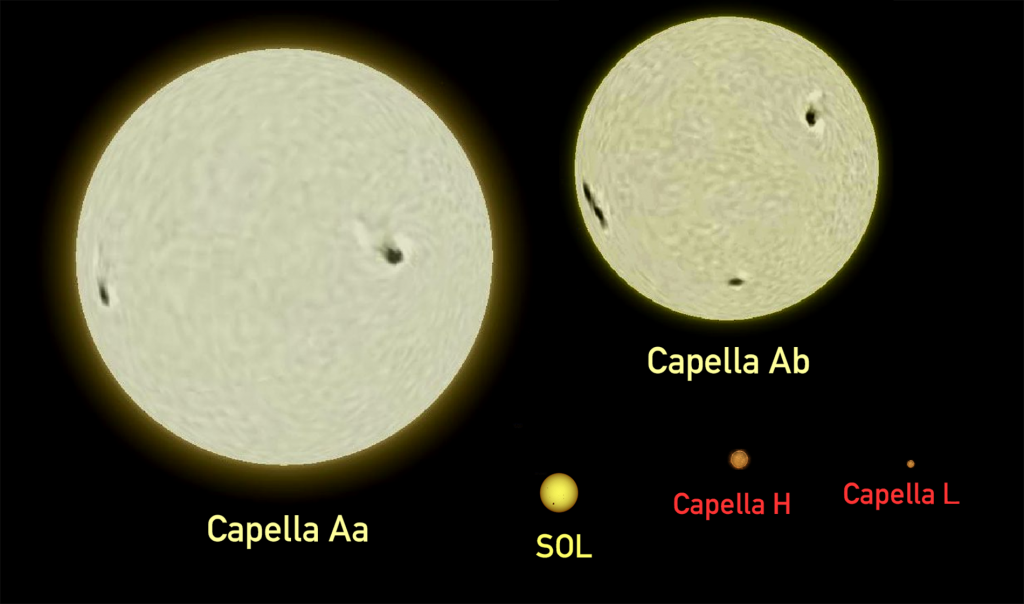
(6) Capella, aka alpha Aurigae, is the most prominent Star in the constellation Auriga. With an apparent visual magnitude of +0.08, Capella is the sixth brightest of all the sky. It is the first magnitude star closest to the North Celestial Pole, so it is impossible to observe it from latitudes below 40º S. It is located about 42 light-years from Earth and is a multiple star system composed of two binaries.
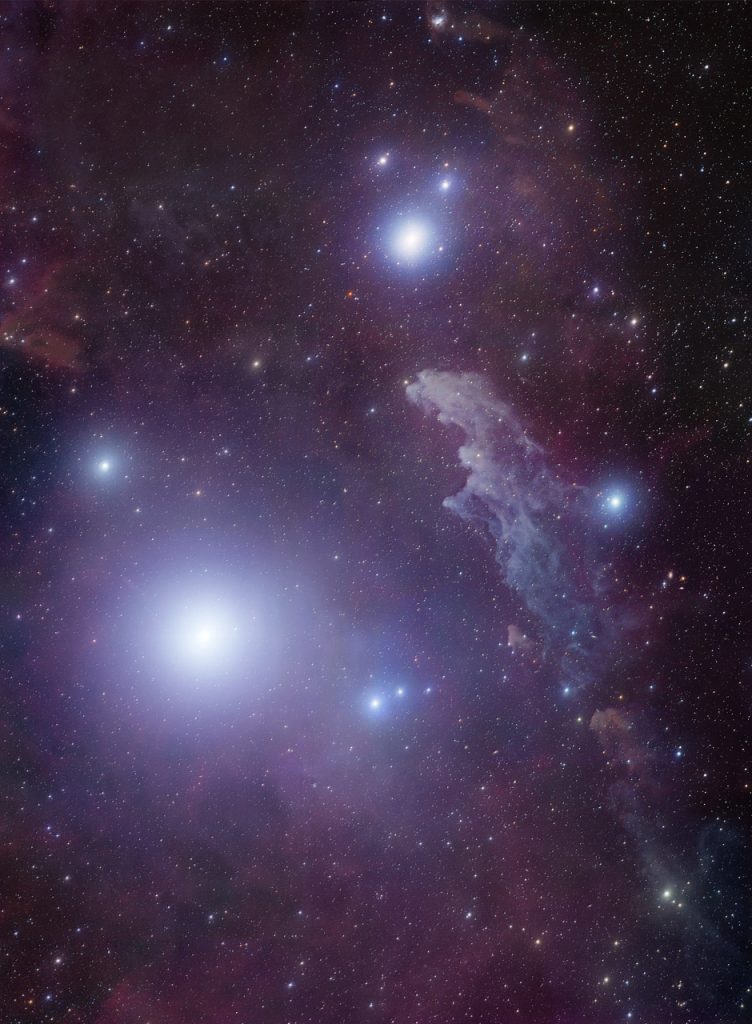

(7) Rigel, aka Beta Orionis, is the seventh brightest Star in the night sky. The brightest in tOrion’sconstellation Rigel has an average apparent magnitude of 0.13 and is a luminous object located around 863 light-years away from Earth.
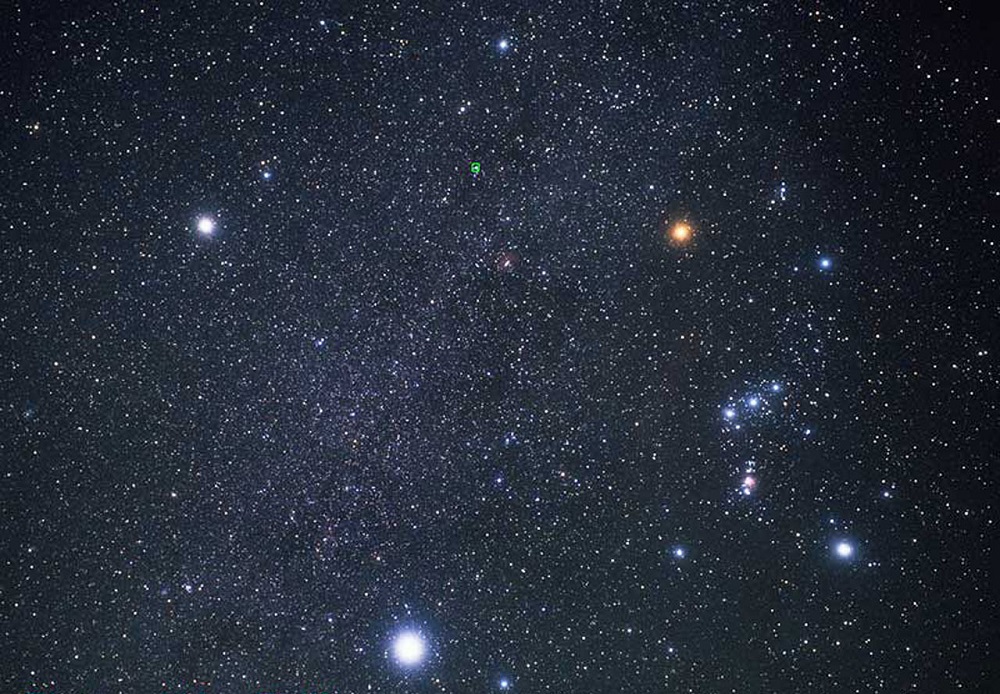

(8) Procyon, better known as Alpha Canis Majoris, is the brightest cosmic object located in the constellation of Canis Minor. It is the eighth-brightest Star in the night sky and has a visual apparent magnitude of 0.34. Located at a distance of just 11.46 light-years, Procyon is, therefore, one of Earth’s nearest stellar neighbors.
(9) Achernar, also designated Alpha Eridani is the ninth brightest Star in the night sky. It is located in the constellation of Eridanus. Located at a distance of 139 light-years from Earth, Achernar is in the deep southern sky and never rises above the horizon beyond 33°N.
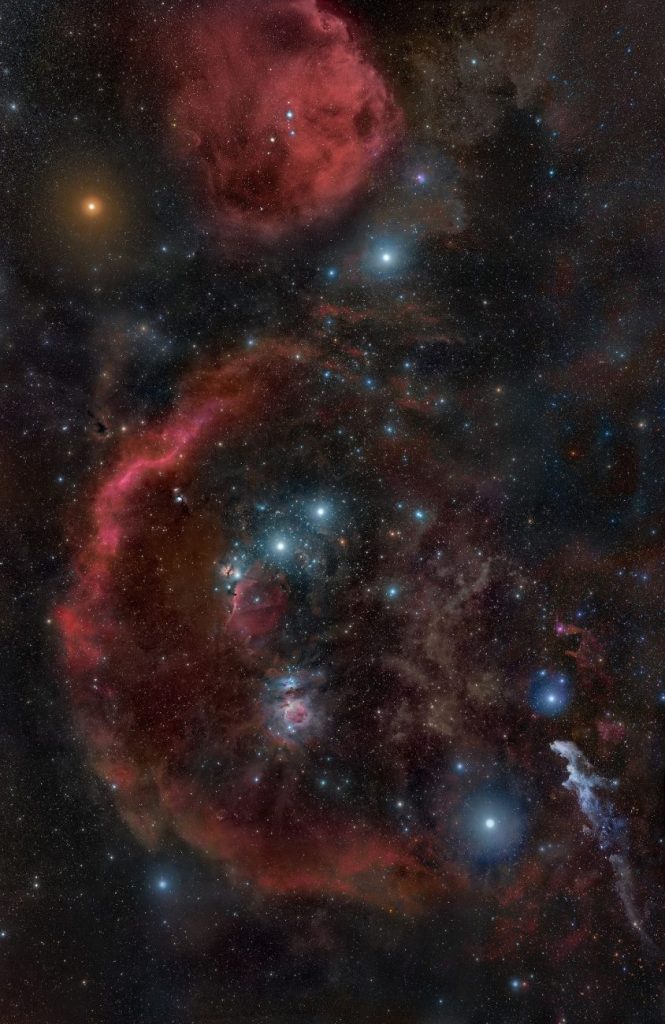

(10) Betelgeuse, also dubbed Alpha Orionis is the tenth brightest Star in the night sky, located in the constellation of Orion. It is the second brightest Star in the constellation of Orion. The Star is massive. According to astronomers, Betelgeuse is a red supergiant of spectral type M1-2. It happens to be one of the largest stars visible to the naked eye. If Betelgeuse were at the center of the Solar System instead of our Sun, its surface would most likely extend past the asteroid belt and the inner planets, completely devouring the orbits of Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, and even possibly Jupiter.

(11) Hadar, more commonly known as Beta Centauri, is s a triple star system located in the southern constellation of Centaurus. Hadar’s combined apparent visual magnitude of 0.61 makes it the second-brightest cosmic object in Centaurus and the eleventh brightest Star in the night sky. Beta Centauri is located around 390 light-years away from Earth.
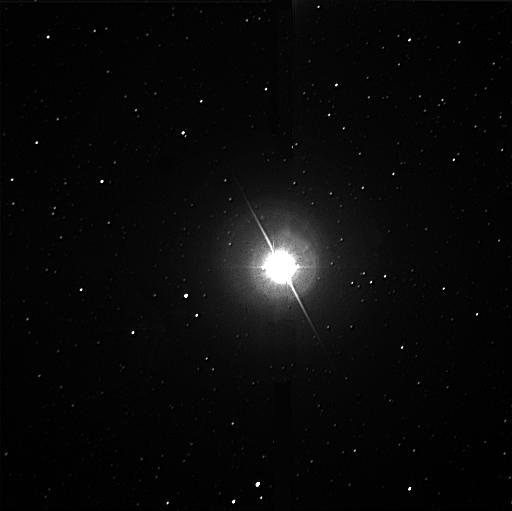

(12) Altair, also designated Alpha Aquilae is the twelfth brightest Star in the night sky. Located around 16.7 light-years from Earth, it is one of the closest stars visible to the naked eye.
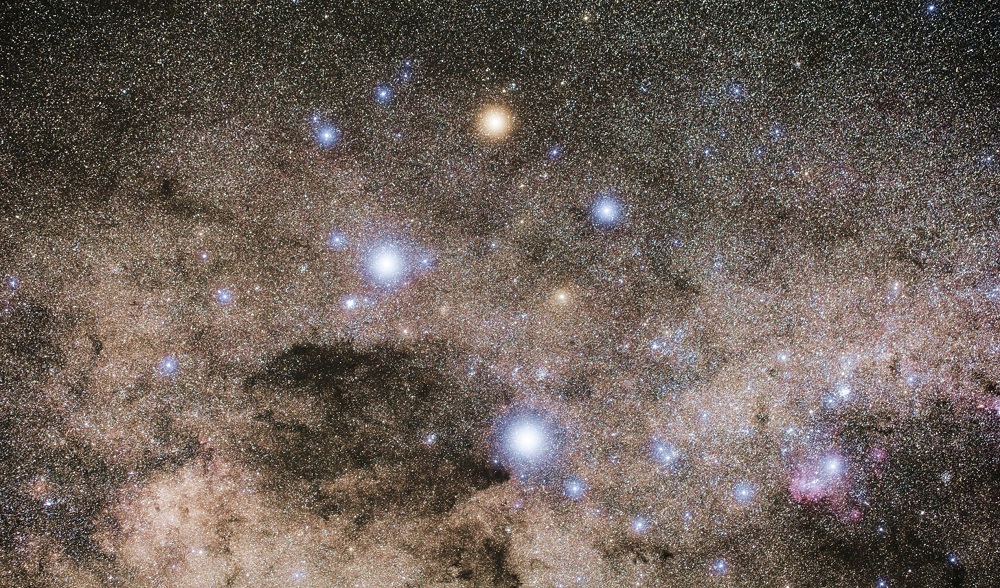

(13) Alpha Crucis is a multiple star system located in the constellation of Cruxis, some 321 light-years away from Earth. The Multiple star system is part of the asterism known as the Southern Cross. Alpha Crucis has a combined visual magnitude of 0.76, and it is the brightest object in Crux and the thirteenth brightest Star in the night sky.
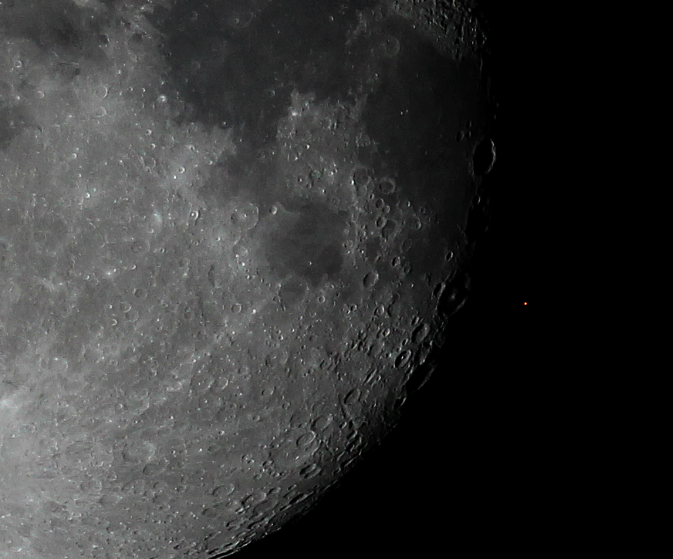

(14) Aldebaran, also known as Alpha Tauri, is a red giant located in the constellation of Taurus. Aldebaran is located around 65 light-years away from Earth and is the fourteenth brightest Star in the night sky. Curiously, Pioneer 10 is currently traveling towards Aldebaran and should make its closest approach in more or less two million years.
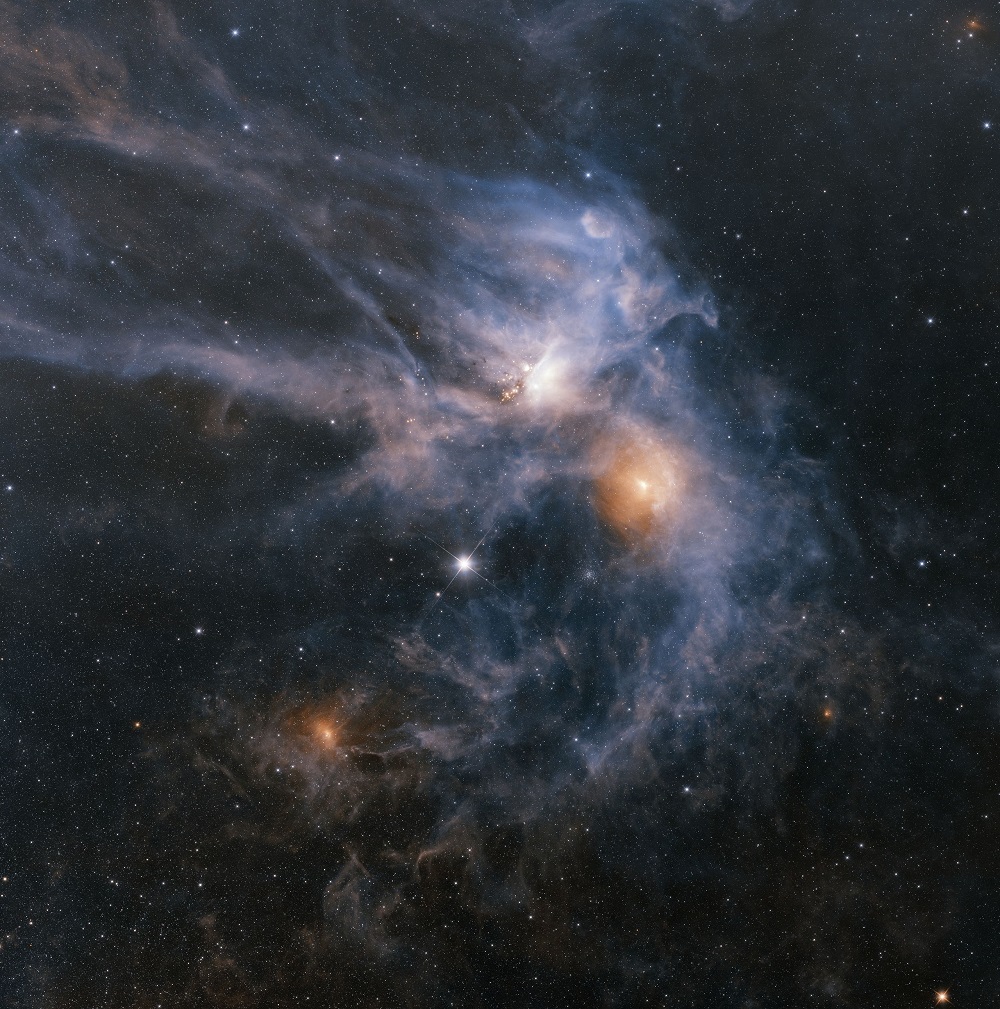

(15) Antares, aka Alpha Scorpii, is the fifteenth-brightest Star in the night sky observed from Earth.
Antares is the brightest object in the constellation of Scorpius.
Join the discussion and participate in awesome giveaways in our mobile Telegram group. Join Curiosmos on Telegram Today. t.me/Curiosmos





