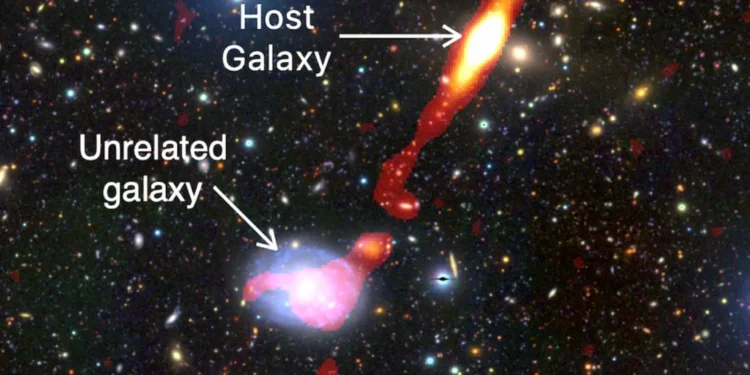
A groundbreaking discovery has left astronomers puzzled: a giant radio galaxy (GRG) nicknamed Inkathazo. This behemoth spans an extraordinary 3.3 million light-years, making its plasma jets 32 times larger than the Milky Way’s diameter. What sets Inkathazo apart, however, is not just its massive scale but the peculiar and unexpected characteristics that challenge established scientific theories.
A “Troublesome” Giant in an Unlikely Place
Named Inkathazo, which means “trouble” in isiZulu and isiXhosa, this galaxy lives up to its moniker. Unlike most GRGs that exist in relatively quiet regions of space, Inkathazo is located at the heart of a dense galaxy cluster, an environment typically unsuitable for the formation of massive radio jets. Yet, it thrives—projecting its enormous plasma jets across cosmic distances.
Adding to the mystery, the jets themselves are far from ordinary. One of them takes an unexpected bend, deviating from the typically straight configurations seen in other GRGs. This unusual behavior has left scientists scrambling for answers.
Kathleen Charlton, the study’s lead author and a graduate researcher at the University of Cape Town, sheds light on the challenges:
“We nicknamed this giant galaxy ‘Inkathazo’ because it has been a bit troublesome to understand the physics behind what’s going on here.”
Unlocking the Secrets with MeerKAT
The discovery of Inkathazo was made possible by the MeerKAT radio telescope, a state-of-the-art instrument based in South Africa. MeerKAT’s exceptional sensitivity allowed astronomers to map the plasma jets in remarkable detail, revealing not only their structure but also their ages.
Interestingly, researchers discovered a stark difference in the plasma’s age on either side of the galaxy. One jet is significantly younger, suggesting ongoing activity or external influences. These findings hint at potential interactions between the jets and the hot gas that fills the galaxy cluster, offering a new window into the complex dynamics of plasma physics.
Dr. Kshitij Thorat, a co-author of the study from the University of Pretoria, explains the implications:
“Finding a giant radio galaxy in a cluster environment challenges our understanding of how these objects form and evolve. It raises intriguing questions about the role of environmental factors in shaping such colossal structures.”
Redefining Galactic Physics
Inkathazo isn’t just a scientific curiosity—it’s an opportunity to rethink existing models of galactic evolution. Its unique traits suggest there’s much more to learn about the behavior of plasma jets and their interaction with intergalactic environments.
This discovery highlights how cutting-edge technology like MeerKAT is transforming our understanding of the universe. But this is just the beginning. The upcoming Square Kilometer Array (SKA), the world’s largest radio telescope, promises to delve even deeper into mysteries like Inkathazo, potentially rewriting the rules of astrophysics.
As part of the next wave of radio astronomy, the SKA will expand upon MeerKAT’s capabilities, providing unparalleled detail of distant celestial objects. Astronomers hope it will not only help explain enigmatic galaxies like Inkathazo but also uncover new phenomena that challenge what we think we know about the universe.
Dr. Jacinta Delhaize, an astrophysicist and co-author of the study, expresses her excitement about what lies ahead:
“While MeerKAT has been a game-changer, the SKA will take us even further, unlocking new dimensions of discovery. We’re on the brink of understanding these extraordinary galaxies in ways we never thought possible.”
Join the Conversation!
Have something to share or discuss? Connect with us on Facebook and join like-minded explorers in our Telegram group. For the latest discoveries and insights, make sure to follow us on Google News.