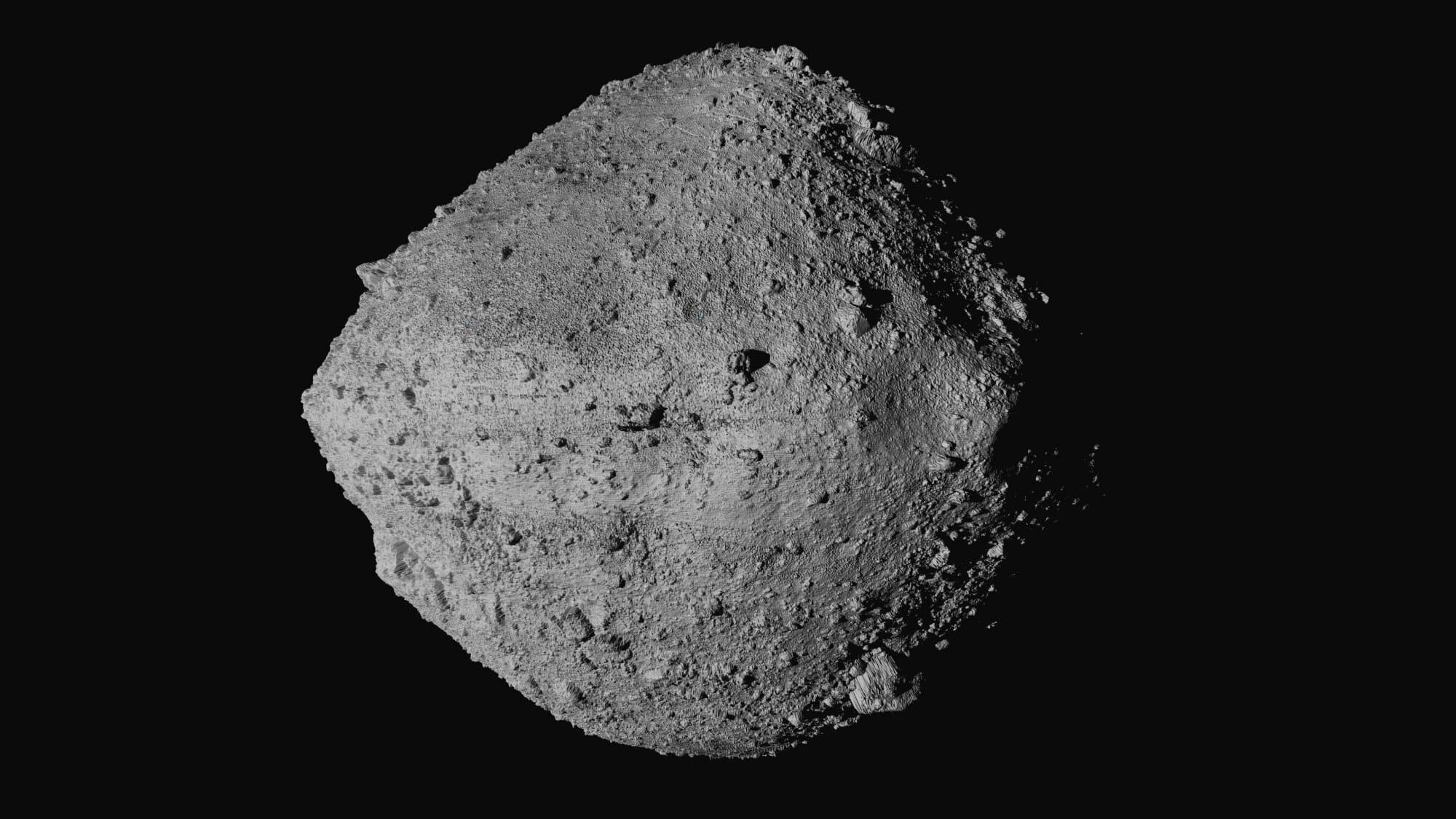
A massive asteroid impact is the stuff of science fiction and disaster movies, but a new study suggests that a collision with a space rock the size of Bennu could have real-world consequences far beyond the initial destruction. Scientists at the IBS Center for Climate Physics (ICCP) at Pusan National University in South Korea have modeled what would happen if a medium-sized asteroid—similar to Bennu—were to crash into Earth. The results? A chilling chain reaction that could reshape the planet’s climate, devastate ecosystems, and trigger a prolonged “impact winter.”
A Rare but Catastrophic Event
Asteroid impacts of this magnitude are rare but not impossible. According to the study, published in Science Advances, Earth is struck by a medium-sized asteroid approximately every 100,000 to 200,000 years. This means that early human civilizations may have witnessed—and survived—these planet-altering collisions. However, the climate shifts and ecological disruptions caused by such an event could have played a crucial role in shaping human evolution.
One of the biggest concerns is asteroid 101955 Bennu, a 500-meter-wide near-Earth object (NEO) that NASA has been closely monitoring. Although Bennu poses no immediate threat, scientists estimate a tiny chance—0.037%—that it could strike Earth in 2182. While the odds remain low, the potential devastation is undeniable.

The Immediate Aftermath: A World in Flames
If an asteroid like Bennu were to impact Earth, the immediate effects would be catastrophic. The collision would unleash energy equivalent to thousands of nuclear explosions, carving out a crater several miles wide and sending shockwaves across continents. The heat generated by the impact would ignite wildfires over vast regions, blanketing the sky with smoke and ash. However, the most severe consequences would unfold in the months and years following the impact.
Using advanced climate models, researchers simulated the atmospheric and ecological fallout. Their findings paint a grim picture: the impact would eject enormous amounts of dust, soot, and sulfur aerosols into the stratosphere, blocking sunlight and drastically lowering global temperatures.
Impact Winter: A Deep Freeze That Could Last Years
The study suggests that the planet’s average temperature could plummet by nearly 40°F (22°C), triggering a phenomenon known as “impact winter.” Sunlight deprivation would cripple the process of photosynthesis, the foundation of Earth’s food chains.

Scientists estimate that global plant productivity would drop by as much as 30% almost instantly, leading to widespread agricultural collapse. Crops would wither, herbivores would starve, and carnivores would follow suit, creating a domino effect that could take decades to stabilize. The researchers liken the conditions to those of the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event, which wiped out 75% of Earth’s species—including the dinosaurs—66 million years ago.
A Surprising Twist: The Ocean’s Unexpected Recovery
While terrestrial ecosystems would struggle to survive in an impact winter, the study found that marine ecosystems might rebound in an unexpected way. Phytoplankton, the microscopic organisms that form the base of the oceanic food chain, would initially experience a dramatic decline due to lack of sunlight. However, within just six months, they could begin to recover—and even surpass pre-impact levels.
The reason? The influx of iron-rich dust from the asteroid impact. This nutrient boost could stimulate massive plankton blooms, temporarily offsetting some of the disruptions in the global food chain. In essence, while land-based ecosystems face collapse, the ocean could experience an unexpected surge in biological productivity.
Lessons for the Future: Can We Prevent an Asteroid Disaster?
While the chances of Bennu striking Earth remain low, this research serves as a stark reminder of our planet’s vulnerability to cosmic threats. Unlike past civilizations that faced asteroid impacts with no defense, modern technology offers ways to detect and possibly deflect incoming objects. NASA’s recent DART mission demonstrated that altering an asteroid’s trajectory is possible, marking a significant step in planetary defense.
However, scientists warn that more investment in asteroid detection and deflection technologies is necessary. Early detection could give humanity a fighting chance to prevent such a catastrophe before it unfolds.
This study doesn’t just highlight the devastation an asteroid impact could cause—it also provides critical insights into Earth’s past and future. From potential mass extinctions to unexpected oceanic recoveries, the research underscores the fragile balance of our planet’s ecosystems.
As space agencies continue to track near-Earth objects, one question remains: Are we prepared for the next big one?
Join the Conversation!
Have something to share or discuss? Connect with us on Facebook and join like-minded explorers in our Telegram group. For the latest discoveries and insights, make sure to follow us on Google News.










