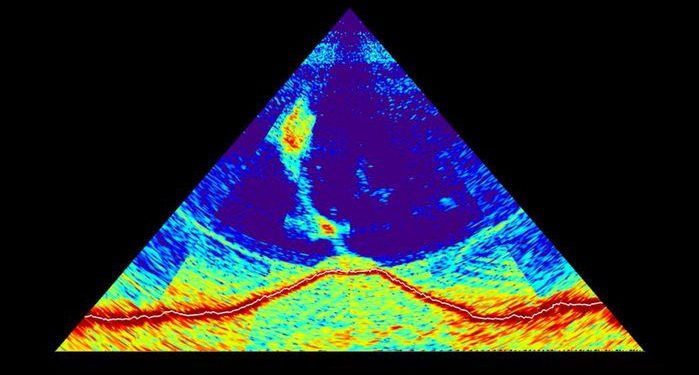
In 2018, the entire planet rang like a bell. Seismometers around the globe recorded the mysterious phenomena, and experts were left stunned. Only now do we know what happened and what seismometers across the world recorded.
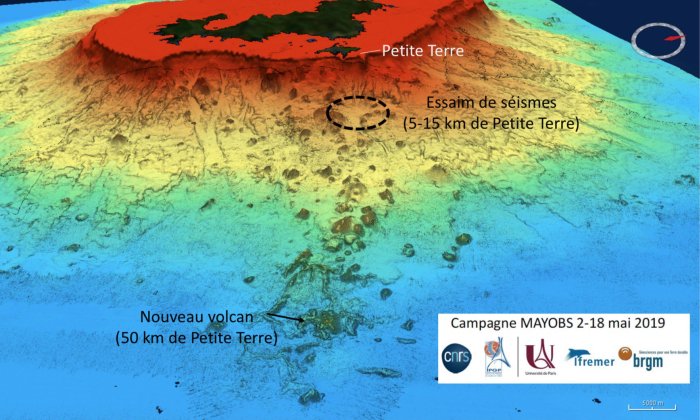
Researchers have reported that an underwater eruption has just given rise to a brand-new volcano, 800 meters high, with a base of around five kilometers.
The entire formation process caused more than 2,000 earthquakes to appear near the Island of Mayotte, caused the entire planet to ring like a bell.
One of the most significant geological events recorded in history has generated the birth of a new volcano about 800 meters high with an approximate base of around 5 kilometers, reports the National Geological Survey of France.
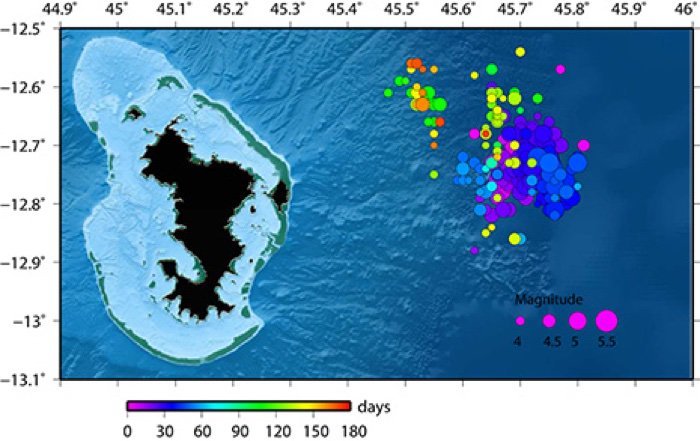
Experts call it the most significant underwater eruption ever observed, which took place in the Indian Ocean. It may be the cause of a series of 2,000 earthquakes that have shaken the volcanic island of Mayotte for the past twelve months.
Since May 10, 2018, successive earthquakes were registered in the Comoro archipelago between Africa and Madagascar.
According to the National Geological Survey of France, the strongest earthquake was of a recorded magnitude of 5.8 degrees.
The unusual telluric activity in the area caught the attention of French geologists, who monitor the site continuously.
However, it wasn’t until November 11 that something extraordinary happened that caused researchers to gather around the phenomenon and try and understand what was going on.
In November of 2018, the Earth rang like a bell.
In November 2018, a low-frequency sound was recorded by experts around the globe. It was as if the Earth rang like a bell. The event continued for more than 20 minutes, and sensors around the globe, as far as 18,000 kilometers from the epicenter, listened to the sound. It was something that had never been registered before.
In February 2019, a team of scientists from the National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS) in France boarded the research vessel, Marion Dufresne, to find the origin of the chain of geological events.
Geologists placed six seismometers at the bottom of the ocean, over 2 miles (3.5 km) down. The scientists then used multibeam acoustic sensors to map the ocean floor. Researchers also pulled up rocks and examined them for any changes.
“They were popping as we brought them on board,” reveals Nathalie Feuillet, director of the Institute of Geophysics in Paris (IPGP) and expedition leader, in an interview with Science.
These ‘popping rocks’ show that high-pressure gas was trapped within the black volcanic material. The devices gathered data until May. Now, scientists have recovered the devices and processed the data they fathered.
They found it fascinating: a magma chamber had ejected molten rock on the seafloor, causing the Earth’s crust to break and a volcano to rise from the ‘underworld.’
According to a press release from the French government, the new underwater volcano “is located over 3,500 meters (2.1 miles) deep. Its current size is 800 m in height (around half a mile) with a base of 4 to 5 km (2.4 miles to 3.1) in diameter. The plume of volcanic fluids 2 km (1.2 miles) in height does not reach the water’s surface.”
Given that the plume of volcanic material only reached about 2 kilometers upwards, nothing was visible on the surface. “We’ve never seen anything like this,” concluded Feuillet.
Join the discussion and participate in awesome giveaways in our mobile Telegram group. Join Curiosmos on Telegram Today. t.me/Curiosmos