It is unimaginable how much of our modern life has been influenced by ancient civilizations.
Following my previous articles on Mesopotamian and Chinese inventions, the time has come to discuss the numerous significant Roman inventions that changed not only life in the ancient world but generally can be considered as predecessors to important modern inventions or have remained in use 2000 years later.
1. Books

Of course, there are many older methods of recording information, such as the Egyptian scrolls and many others, but the book, as we know it to a large extent today, is one of many Roman inventions.
It is unknown exactly when and how, but the codex, which literally means a cube of wood, appeared in the Roman Empire in the 1st century AD. The first books were called codex precisely because of the hardcovers that protected the pages on both sides.
Nevertheless, the Romans continued to use the old method of scrolls for at least another 3 or 4 centuries before books became the standard recording format.
3. Roads as we know them
It would be impossible and improper to consider that one person could be behind creating the roads in general. Roads existed long before the Romans, and honestly, any path that had been used numerously by ancient people can be considered a road.
However, carefully build and structured roads are definitely one of the greatest Roman inventions. They needed to create such a network given the immense size of the Roman Empire. In fact, scholars have calculated an estimate of over 400,000 kilometers of built roads that connected all the provinces in the Roman Empire.
4. Cement and concrete
The ancient Roman civilization advanced in literally every aspect, and their architecture is an absolute wonder. While the creator or founder of these materials is unknown, it is a fact that much of Rome was built with concrete, and concrete cannot exist without cement. It is because of these materials that so many Roman cities and monuments survived to modern days.
For example, I can give the Great Fire that burned down almost the entire city of Rome in 64 AD. Historians debate whether this was an act of Emperor Nero, searching for a reason to rebuild one stronger Rome, or it was a natural disaster.
Nevertheless, much of Rome at that time was built from weaker materials, which led to the ultimate destruction of many parts of the city. Only the several newer neighborhoods made from concrete survived the great fire.
5. Shopping Malls
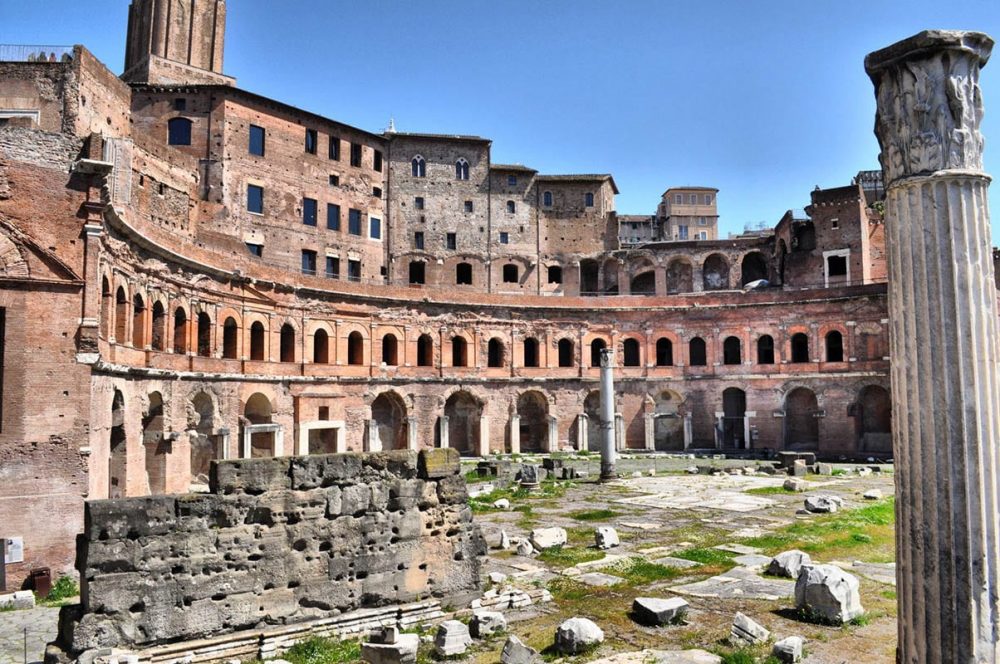

Have you heard of Trajan’s Market? It is considered to be the oldest shopping mall in the world, and it too has remained intact and can be seen today in Rome.
It was constructed between 110 AD and 115 AD, and it supposedly held more than 150 shops and offices. It had stores in the lower levels and offices and administration on the upper levels, similar to modern shopping centers.
6. High-rise buildings and apartments

In a striking similarity to the modern way of dealing with overpopulation, the Romans began building high-rise blocks. It is said that there were tens of thousands of these buildings in Rome, called Insulae.
They were typically 2-3 floors high, although some reached the impressive nine floors in height. As you can probably guess, these were made for the majority of the population that was poor, and the overall architecture included cheaper materials like wood.
7. Postal services
Once again, the Roman Empire’s size influenced yet another incredibly significant Roman invention – postal services. With the addition of the sophisticated road network, Emperor Augustus founded the first-ever postal service known in history.
This system included couriers who were either regular people or even soldiers, who carried messages and packages from one major city to another. Of course, this postal network did not include small villages and towns, but it was generally available in forts and major cities throughout the empire.
2. Public Newspapers

Of course, this does not mean that the Romans sold newspapers as we know them today, but they did invent a method to keep the public informed about the Roman Empire’s latest events.
More of an invention of the Roman Republic, I put this on the list as it emerged around the time when the Roman Republic was re-arranged into an Empire.
The Roman newspaper was called Acta Diurna, which literally means Daily Acts. It was presented on large stone slabs that were updated daily and placed in public squares and locations accessible to the public.
The Acta Diurna contained information about religious events, law, future celebrations, and even astrological readings. These stone slabs have become a significant historical source for scholars since the Romans stored them in archives, and many have remained to this day.
8. Sewer systems
Perhaps you have heard of the Roman aqueducts. Many remain intact in various locations in Europe and Asia Minor. They had the purpose of bringing clean fresh water to the Roman cities but also removing waste. This is how the ancient Roman sewer systems were invented.
They built sophisticated sewer systems and then used the water from the massive aqueducts to flush the waste away and replace it with clean water.
9. Surgery tools
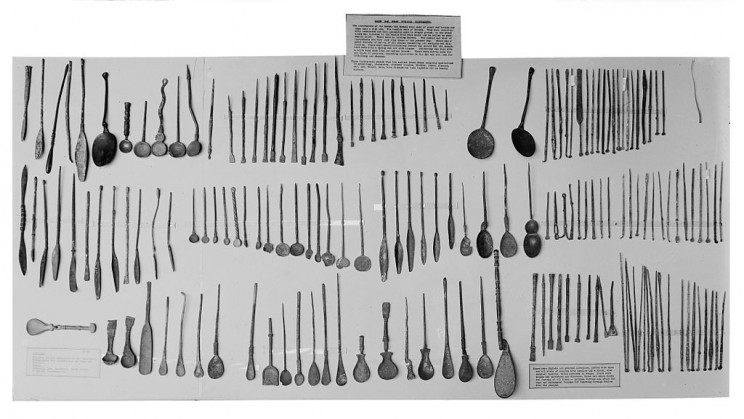

Yes, surgeries have been performed since the dawn of humanity. Even the most ancient civilizations had their own medicines and practices but surgical tools as we know them today are another Roman invention.
As it seems, Emperor Augustus was a truly dedicated ruler as many of the greatest Roman inventions appeared during his reign. He founded the Roman military medic corps, which were sent to the battlefield to treat injured soldiers.
He also influenced the creation of many surgical tools that modern medicine continues to use today—for example, obstetric hooks and scalpels.
10. Modern Laws
If you decide to dig deep into the ancient Roman laws, you will see striking similarities to most laws we have and utilize today. All ancient civilizations and cultures, in general, had certain laws, but Rome took its legal system to the next level.
It would take a separate article to discuss Roman laws as a whole. Still, I can give a few simple examples of acts that remain in use in modern legal systems – habeas corpus, the affidavit document, and pro bono Publico.
Join the discussion and participate in awesome giveaways in our mobile Telegram group. Join Curiosmos on Telegram Today. t.me/Curiosmos











