The idea that the atmosphere of the Earth extends beyond the moon might sound like science fiction—but it’s real. And it’s quietly changing how scientists define the very edge of our world. And when you think about it in a literal sense, it measn that the astronauts that set foot on the Moon during the Apollo misions never actually left the atmosphere of the Earth.
For most of modern history, the boundary between Earth and space was drawn at the Kármán line, around 100 kilometers above sea level. But recent studies of old satellite data reveal that Earth’s atmosphere continues far past that invisible border—stretching more than 630,000 kilometers into space. That’s over 50 times the diameter of the planet itself. And yes, that means the Moon—on average about 384,000 kilometers away—is still within Earth’s atmospheric reach.
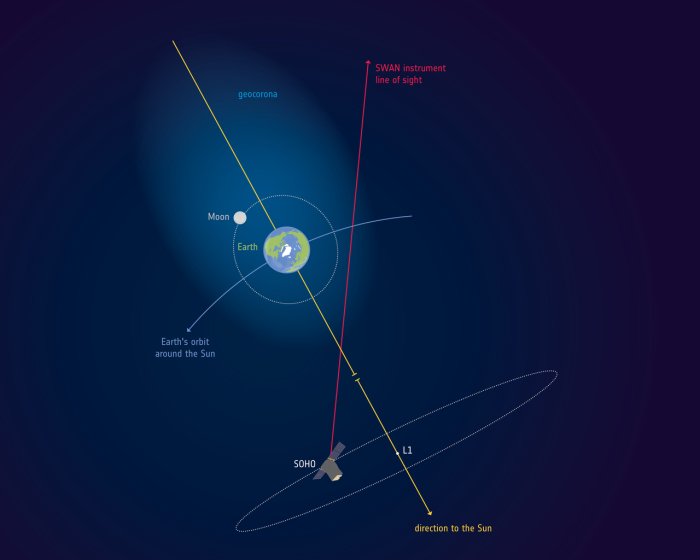
The invisible halo called the geocorona
The discovery centers around a region called the geocorona, which marks the outermost boundary of the exosphere—the final layer of Earth’s atmosphere. It’s composed of neutral hydrogen atoms so thinly scattered that they’re nearly impossible to detect. But thanks to their ultraviolet glow, they left a signature in space.
Between 1996 and 1998, the SOHO spacecraft—a joint mission by NASA and the European Space Agency—gathered ultraviolet light data using its SWAN instrument. That data sat largely ignored for years until researchers took a closer look and realized just how far the atmosphere actually extended.
They found that the geocorona stretches roughly 630,000 kilometers from Earth, enveloping the Moon and challenging the textbook definition of where Earth ends and space begins. Even more surprising? Astronauts from Apollo 16 photographed the geocorona from the lunar surface in 1972—completely unaware that they were still technically within Earth’s atmosphere.
If the atmosphere of the Earth extends beyond the Moon, what is space?
This new understanding blurs the line between our planet and outer space. It raises questions about what it means to “leave Earth,” and whether any astronaut has ever truly exited the planet’s atmospheric grasp.
The geocorona is far too diffuse to affect spacecraft or missions in practical terms. But conceptually, it changes everything. We used to picture the atmosphere as a blanket wrapped tightly around our planet. Now we know it’s more like a fading whisper that reaches out across space. And that fading whisper matters.
Rethinking planetary boundaries and searching for life
Knowing that the atmosphere of the Earth extends beyond the Moon also reshapes how we study other planets. When astronomers analyze the thin gas envelopes around distant exoplanets, they’re often looking for UV signatures—just like the ones from our geocorona. If similar halos surround other rocky worlds, they may provide clues about those planets’ compositions, weather systems, or even their potential to support life. And back here on Earth, understanding the full extent of our atmosphere could help scientists refine satellite trajectories, radiation exposure models, and long-range space mission planning.
We often think of the Moon as a distant world, but in a very real sense, it still sits within Earth’s reach. Not physically. Not magnetically. But atmospherically. Knowing that the atmosphere of the Earth extends beyond the moon changes how we think about our planet. It’s not just a solid sphere floating in space—it’s surrounded by a vast, invisible layer that stretches farther than we ever imagined.











