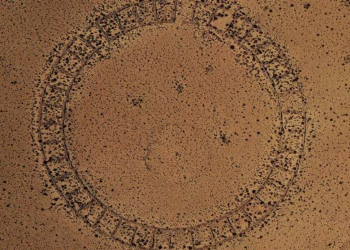
The first cultures of the Amazon created thousands of artificial forest islands while domesticating wild plants to grow food, effectively terraforming various regions of the Amazon rainforest, according to a new study from the University of Bern published in the journal Nature.
The discovery is the most recent evidence showing the great impact people had on the area. Since the arrival of some of the first cultures to the region around 10,000 years ago, societies terraformed the landscape when they started growing cassava and squash.
Scientists found that this led to the creation of 4,700 forest islands (forest islands because they now occur as patches of forest surrounded by savannah) in what is now Llanos de Moxos in northern Bolivia. This area is flooded from December to March and is extremely dry from July to October, but the mounds remain above water level during the rainy season, allowing trees to grow on them. The mounds improved the diversity of the landscape and show that small-scale communities shaped the Amazon 8,000 years earlier than previously thought.
Terraforming the Amazon
“Recent genetic and archaeological evidence suggests the existence of at least four independent centers of domestication in the early Holocene epoch, two in the Old World (Near East and China) and two in the New World (southwestern Mexico and northwestern South America). However, the closest wild ancestors of several globally important domesticated cultigens occur in southwestern Amazonia,” the researchers wrote in the study.
“Sixty-six accelerated mass spectrometry radiocarbon dates from 31 archaeological sites bracket the human occupation of forest islands throughout the Holocene epoch to between about 10,850 and 2,300 years ago. The dated sites—except for three sites in the northeastern Llanos de Moxos, two of which are dated to 2,350 and one to 4,100 years ago—were established between the early and mid-Holocene epoch,” the researchers explained.
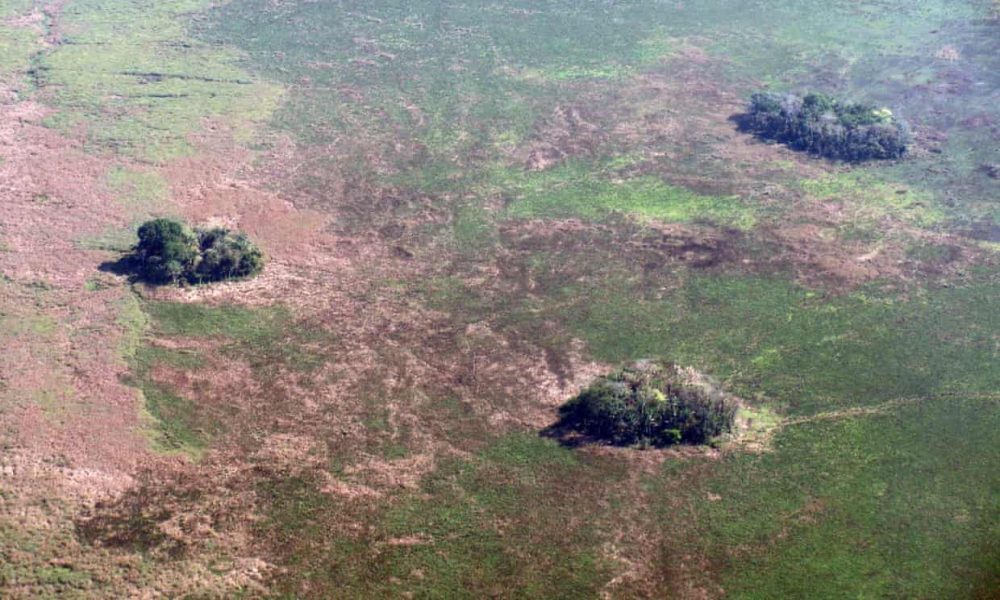

The Amazon is one of the world’s first centers of plant domestication
New surveys and studies have confirmed that this part of the Amazon is one of the world’s first centers of plant domestication. Using microscopic bodies of plant silica, called phytoliths, which are well preserved in tropical forests, experts have documented the earliest evidence found in the Amazon of cassava 10,350 years ago, squash 10,250 years ago, and corn 6,850 years ago.
Plants grown on the Amazonian forest islands were chosen because they were carbohydrate-rich and easy to cook and likely provided a considerable portion of the calories consumed by the region’s earliest inhabitants, supplemented by fish and meat. The study was carried out by Umberto Lombardo and Heinz Veit from the University of Bern, Jose Iriarte and Lautaro Hilbert from the University of Exeter, Javier Ruiz-Pérez from the Pompeu Fabra University, and José Capriles from the Pennsylvania State University.
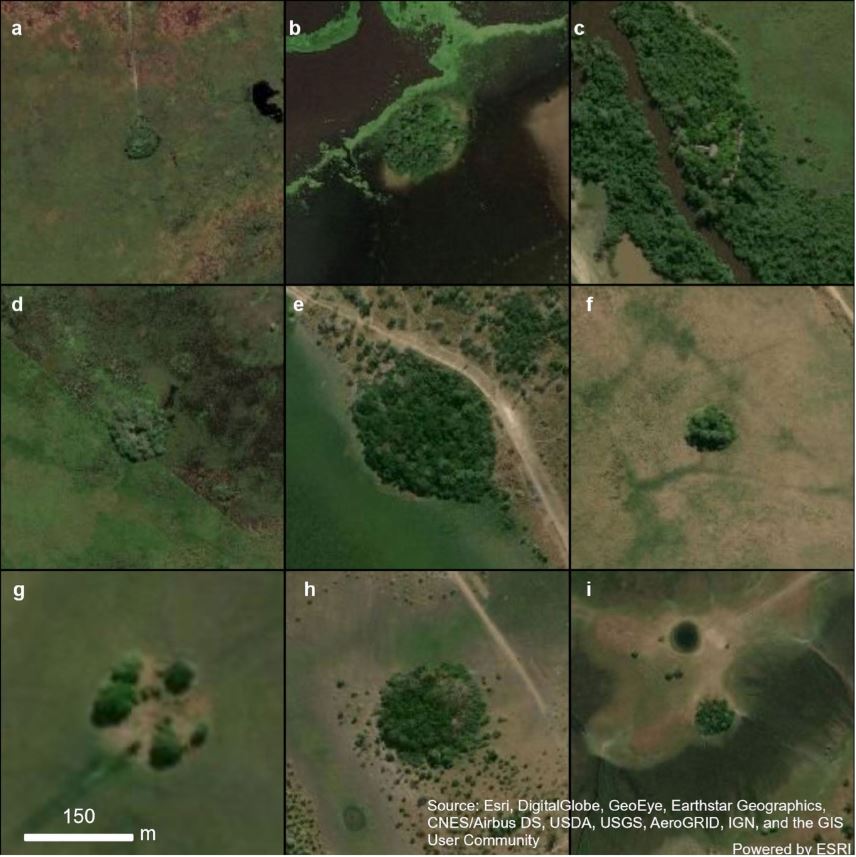

Major cultivars
The study includes an unprecedented large-scale regional analysis of 61 archaeological sites (some of which are now forest patches surrounded by savannas) identified by remote sensing. Samples were recovered from 30 forest islands, and four archaeological excavations were carried out. “Our results confirm the Llanos de Moxos as a hotspot for early plant cultivation and show that since their arrival, humans have caused a profound alteration of Amazonian landscapes, with lasting repercussions for habitat heterogeneity and species conservation,” the researchers revealed.
Scientists have argued for many years that the Southwest Amazon was a likely center of early domestication of plants because many major cultivars such as cassava, squash, peanuts, and some varieties of chili and beans are genetically very near to wild plants that live here. However, until this recent study, scientists had not searched for or excavated ancient archaeological sites in this region that could document the pre-Columbian domestication of these crops.
Have something to add? Visit Curiosmos on Facebook. Join the discussion in our mobile Telegram group. Also, follow us on Google News.