Tenochtitlan, the great capital of the Mexica (as the Aztecs referred to themselves), became one of the most important cities in the pre-Hispanic world. The city was so advanced, well-designed, and intricately built that upon arriving in the city, the Spanish said it was the most beautiful city they had encountered, comparable to Venice. In fact, Tenochtitlan would later become known as the Venice of the New World.
The origin of the city of Tenochtitlan is a mixture of reality, mythology, and spirituality. After a pilgrimage of more than 200 years where the Aztec journeyed from northern parts of Mesoamerica, the Mexica reached the Basin of Mexico, then known as Anahuac. Around the year 1325, it is believed that the Mexica settled on an islet in Lake Texcoco, where they lived in exchange for paying tribute to the Tepanecs of Azcapotzalco. This is where the history of Tenochtitlan begins to become a legend since Huitzilopochtli, one of the main gods of the Mexica, supposedly communicates with a priest of the Mexica during the voyage to the south and sends a sign that the Aztecs should finally settle, building their new city.
This divine sign consisted of an eagle standing on a cactus, devouring a snake. In the place where the Mexica found this sign, they founded the city of Mexico-Tenochtitlan and built a pyramid known today as Templo Mayor.
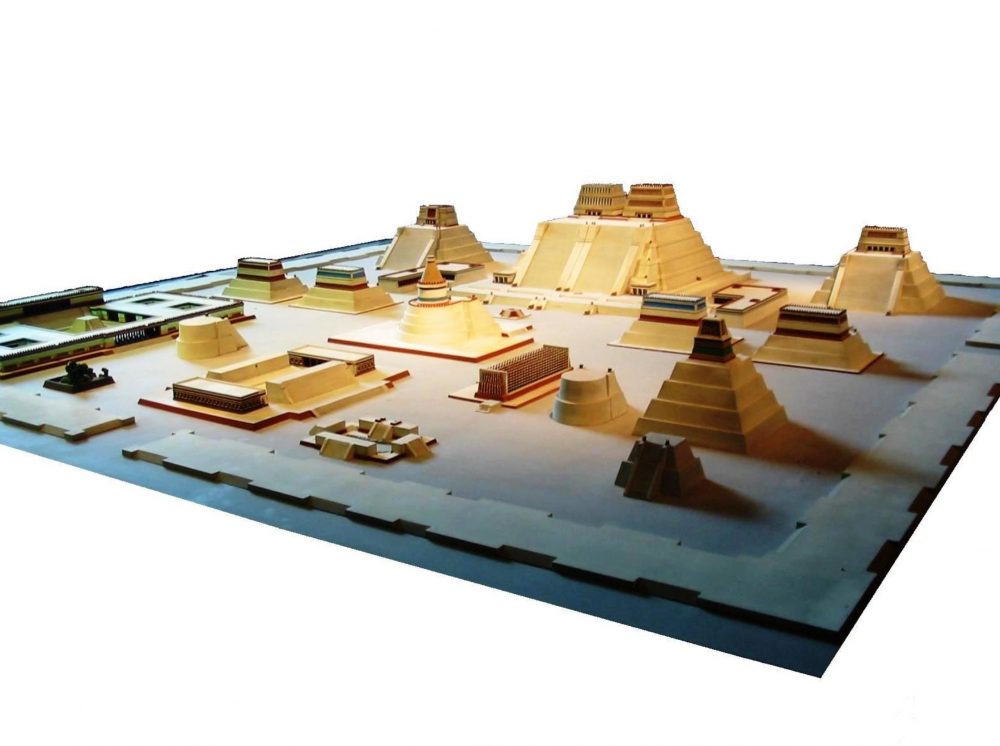

Tenochtitlan inspired by Teotihuacan
When the Mexica arrived in the Valley of Mexico in the 13th century, Teotihuacan was already centuries extinct. Its massive pyramids were covered in ruins and overgrown. These were vestiges of a formerly great civilization. According to archaeologist and anthropologist Eduardo Matos Moctezuma in his book Tenochtitlan, The Aztecs found its remains and, not knowing who had built it, attributed its creation to the gods. Their admiration was so great that they copied the previous layout for the new city. Evidence of this is more than 40 objects believed to have originated at Teotihuacan, found among the ruins of Templo Mayor. This tells us that the Mexica helped Teotihuacan in high regard.
The first thing that the Aztecs built in Tenochtitlan was a temple
The first thing the Aztecs did, once Huitzilopochtli indicated the appropriate site to found the new city, was to build a temple to honor this god. The Aztecs built their most prominent temple, a pyramid known today as Templo Mayor in the exact spot where they saw an eagle standing on a cactus, devouring a snake.
The Templo Mayor, the jewel of Tenochtitlan
The Templo Mayor—Tenochtitlan’s great pyramid, was the most important religious site of the Mexica; it was located at the crossroads of the two main axes of the city and was the central feature of the city. The Templo Mayor would eventually be destroyed after the Spanish conquered the city, as they were making room for a cathedral.
Tenochtitlan was divided into four sectors
Leaving the Huitzilopochtli temple to the center, the new city was divided into four main neighborhoods: Moyotlan, Teopan, Atzacualco, and Cuepopan.
The Aztecs built four great causeways
Just after dividing the city into four specific sectors, the ancient Aztecs proceeded to create four causeways that were oriented towards the four cardinal points. That of Tepeyac was to the north, that of Iztapalapa to the south, that of Tacuba to the west, and there was a smaller one to the east.
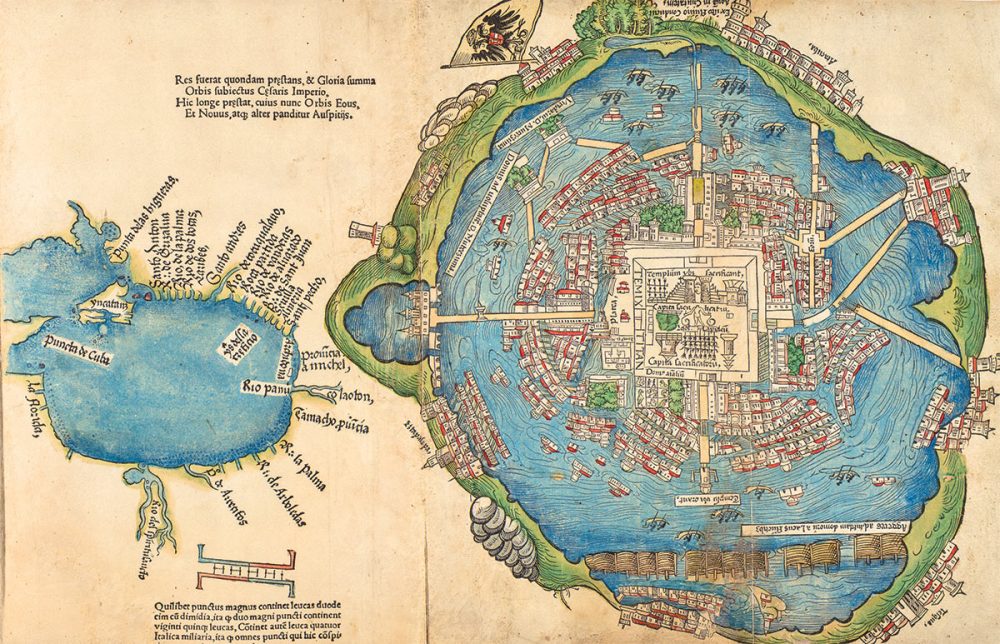
An intricate hydraulic system
When the Spanish conquerors arrived in Tenochtitlan, they realized that the Mexica had built an excellent hydraulic system since they had to prevent the salty water from flooding the city. This hydraulic system also allowed them to channel fresh water for human consumption.
Tenochtitlan had a twin city
A few people know that, a few years after creating the settlement of Tenochtitlan, a group of dissatisfied settlers separated from the original group and founded, in 1337, the city of Tlatelolco, which would become a rival of Tenochtitlan.
Acamapichtli, the first tlatoani (ruler)
Around 1368 the priest Tenoch died, who had led the Mexica on their pilgrimage, so the group was forced to choose a new leader. The people turned to the lord of Culhuacan, Nauhyotl, to choose the first tlatoani of Tenochtitlan. This position would eventually be filled by a man called Acamapichtli, who reigned for 19 years.
Tenochtitlan’s independence
For years after the city was established, the Mexica continued to pay tribute to the people of Azcapotzalco. The situation between the two towns was tense until, in the 1420s, Tenochtitlan rebelled for its independence and managed to consolidate an alliance with the city of Texcoco.
The Spanish were impressed with Tenochtitlan
Bernal Díaz del Castillo left testimony of the impression that Tenochtitlan left on the Spanish invaders:
When we saw all those cities and villages built on water; and the other great towns on dry land, and that straight and level causeway leading to Mexico, we were astounded. These great towns and shrines and buildings rising from the water, all made of stone, seemed like an enchanted vision from the tale of Amadis. Indeed some of our soldiers asked whether it was not all a dream. It is not surprising therefore that I should write in this vein. It was all so wonderful that I do not know how to describe this first glimpse of things never heard or, never seen, and never dreamed of before.
Check out the featured image artwork here.
Join the discussion and participate in awesome giveaways in our mobile Telegram group. Join Curiosmos on Telegram Today. t.me/Curiosmos











