The Step Pyramid of Djoser has been reopened to the public after 14 years. Explore the core of the Pyramid in three striking videos of the interior of the Pyramid.
Around 4,700 years ago, Egyptian civilization saw a revolution in architecture and design during the Third Dynasty. At the royal necropolis of Saqqara, King Djoser instructed his royal vizier and architect Imhotep to build a unique structure. Until that point, Egyptologists say that tombs in Egypt were made of mud-brick and lesser materials. They used stones, although in very small quantities. The mastabas had remained the tombs of the Egyptians since pre-dynastic times. However, 4,700 years ago, things changed. Imhotep was a young architect with refreshing, revolutionary ideas, and the pharaoh recognized that.
Djoser gave the young architect free hands in designing and building his newest monument. Imhotep did not disappoint. Although most of what we know about the Step pyramid and its intricate pyramid complex is archeological guesswork because of the complete lack of written accounts, some experts believe the Step Pyramid at Saqqara was not intended to be such from the beginning. Considered a proto-pyramid, researchers agree that the monument was built in various stages and took around 19 years to complete. Egyptologists maintain that the Step Pyramid—which started as a square, morphed mastaba—was enlarged and developed every three years.
The steps toward a step Pyramid
Eventually, nineteen years after the first stones were laid on the desert plateau at Saqqara, Imhotep’s masterpiece was finished. Djoser lived long enough to see the monument come “to life.” Djoser’s Step pyramid is regarded as a monument that changed Egypt forever. The intricate stone structure is the earliest colossal stone building and the earliest large-scale cut-stone construction in Egypt. Drawing precedents from various earlier, lesser monuments, the Pyramid is thought to have been erected in six distinctive stages.
Although it resembled a mastaba, it began as a square structure that was never one. The structure was built but enlarged during the first stages. The Pyramid builders led by Imhotep would enlarge the structure evenly on all four sides and just on its eastern part. Experts identify these developments as M1, M2, and M3, respectively. Experts believe the morphed mastaba to have been built in two distinct stages. First, it is thought to have been constructed and shaped to form a four-stepped structure (stage P1) and then form the six-stepped structure (stage P2), with a clear rectangular base aligned on an east-to-west axis.
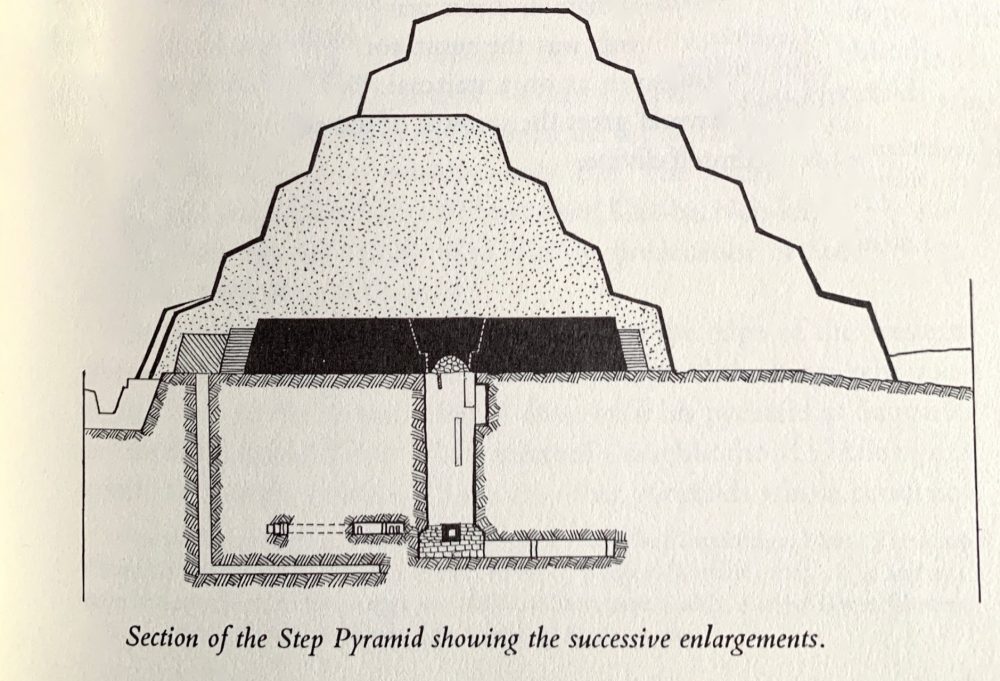
The fact that the Pyramid’s initial structure was square led many experts to suggest the monument designed by Imhotep was never meant to be a mastaba since there are no square mastabas anywhere in Egypt. While this may be accurate, it remains a mystery whether Imhotep initially planned to build a step pyramid.
Videos of the interior of Djoser’s Pyramid
Analysis of the Step Pyramid has revealed great insight into the evolution and appearance of pyramids in Egypt.
Archeological excavations at Saqqara suggest that the project underwent a major construction shift when the builders began transforming the initial “mastaba” into a pyramid made of four steps. Just as in the construction of classical mastabas, the builders would construct a crude core of roughly cut stones, which were cased in fine limestone and packing in between.
https://www.facebook.com/sabrykhalifa/videos/2754685281315512/
However, there was one major difference: The builders would lay horizontal courses in the mastaba building. However, the builders were instructed to build in accretion layers that leaned inwards for the Pyramid. They also sued blocks that were much larger and of greater quality. Essentially, the Step Pyramid is a revolutionary structure in many ways. A project such as Djoser’s Pyramid complex was never attempted in Egypt. Daring, revolutionary, and supermassive, Egyptologists agree that the social implications of such a large and carefully sculpted project are mindboggling.
The completion of the Pyramid proves that the state, and therefore the royal government, had a profound level of control of material resources and workforce as well during the Third Dynasty. The Step Pyramid is impressive on many levels. However, what is perhaps even more fascinating is the secret the Pyramid hides beneath its surface. Around 4,700 years ago, when the Pyramid was not even formed, the builders began excavating beneath the foundations of the Pyramid, creating a behemoth subterranean world.
Not many people are aware of the existence of a massive underground world beneath the Pyramid.
https://www.facebook.com/MWTEgypt/videos/2500183366962289/
A subterranean world
It completely blows my mind that the builders managed to excavate around 5.7 kilometers worth of magazines, tunnels, and chambers, creating the largest, most impressive labyrinth in existence beneath any pyramid. Such a massive underground world would never again be constructed in the history of Egyptian pyramid buildings. Not even the most impressive Pyramid in Egypt, the Great Pyramid of Giza features such an intricate world beneath it. This massive underground network of tunnels is one of the greatest mysteries of the Step Pyramid guards.
Its exact purpose eludes experts, although Egyptologists seem convinced that it was excavated and decorated to serve as King Djoser’s eternal resting place. Curiously, although Egyptologists maintain the Step Pyramid served as Djoser’s tomb, the mummy of the Pharoah has never been discovered. To explain the missing mummy, scholars say that the Step Pyramid and its subterranean world were looted in distant times and that all of its treasures, including the King’s mummy, were stolen.
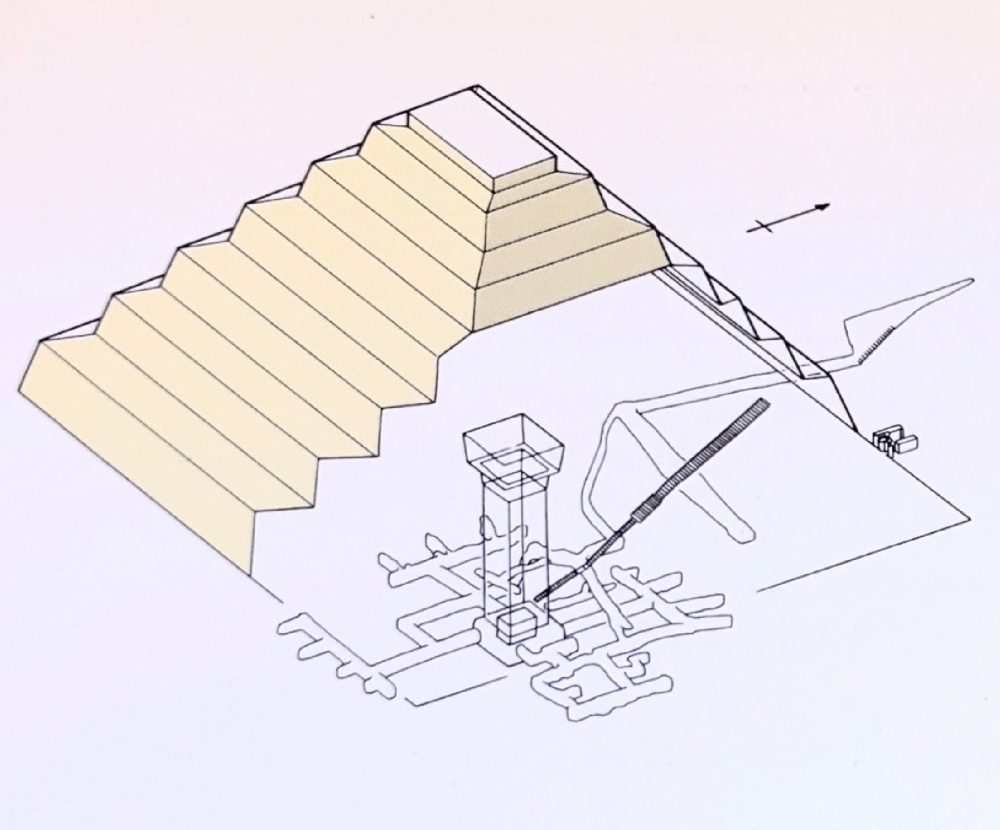
Despite not discovering the mummy of the pharaoh, archeological explorations of the Pyramid did reveal 40,000 vessels in various chambers beneath the Pyramid. Interestingly, many of these vessels were inscribed with Djoser’s ancestors’ names, leading experts to believe that the subterranean world may also have served as a kind of repository of the past. One of the most interesting discoveries made inside the Pyramid was the hipbone of a young female. Curiously, the person to whom the hipbone belongs was found to predate King Djoser by several generations, leaving experts wondering how and why such ancient bones were placed beneath the Pyramid in the first place.
The Step Pyramid of Djoser was built with a total volume of 330,400 cubic meters (11,667,966 cu ft). Its base measures 121 meters (397 ft; 231 cu) by 109 meters (358 ft; 208 cu). Interestingly, in terms of volume, the Step Pyramid is much larger than the Pyramid of Menkaure at Giza, which has a total volume of 235,183 cubic meters (8,305,409 cu ft).
Join the discussion and participate in awesome giveaways in our mobile Telegram group. Join Curiosmos on Telegram Today. t.me/Curiosmos











